CBD products are marketed with low THC content (Low T CBD) or no THC content (T Free CBD). However, removing the psychoactive THC from the CBD can be a challenge.
THC remediation involves the removal or degradation of unwanted THC from CBD. Delayed monitoring is most commonly used when a sample is collected, diluted, and then analyzed by HPLC. When the HPLC analysis shows that the THC level is below the desired threshold or becomes non-detect, the operator stops the remediation process.
By design, delayed monitoring over-processes the material since samples are only taken periodically and the HPLC analysis takes time. This extends the remediation time and leads to unnecessary loss of valuable CBD.
A best practice is to automatically monitor the THC concentration in real-time. Real-time monitoring allows the process to be stopped as soon as the desired THC level is achieved.
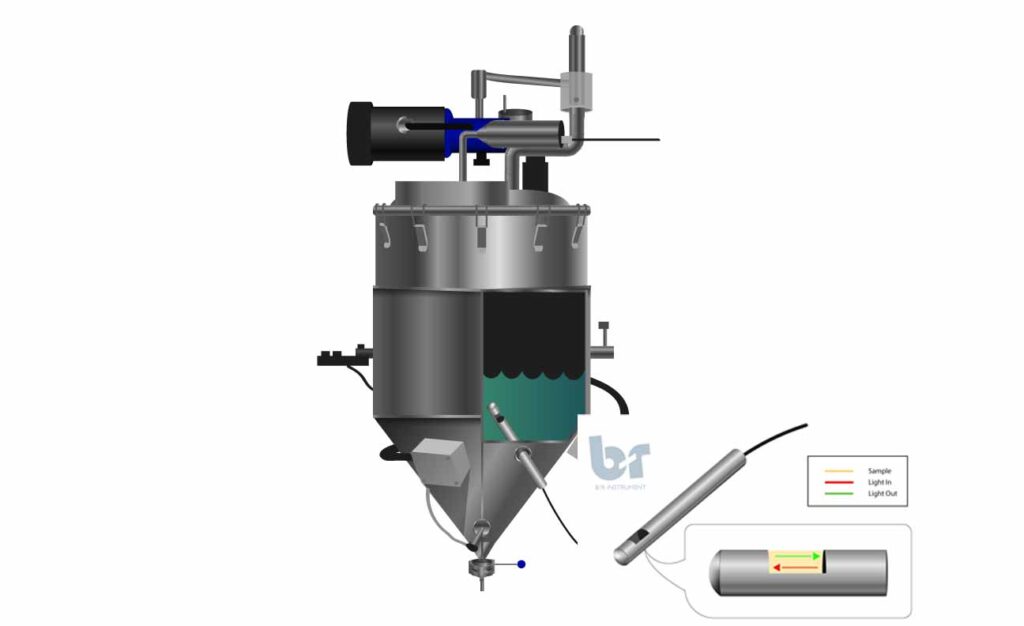
The Near IR probe is mounted so that it is directly in the CBD. No need to take a sample or dilute it for HPLC. The Near IR analyzer monitors the CBD continuously in the reactor.
- No unnecessary loss of additional CBD due to over processing. Shortest possible remediation time.
- Make decisions in real time
- No need for a person to collect samples, dilute samples or a trained HPLC operator
Near Infrared has been around for decades but its application to cannabinoid measurement is fairly recent.
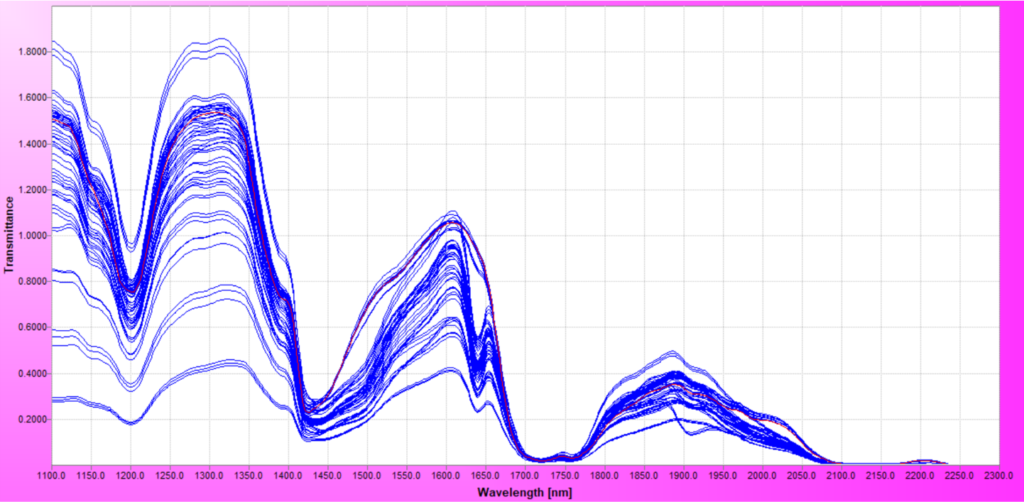
Wavelengths in the Near IR are beamed directly into the CBD during remediation. A detector measures the response of the material to the various wavelengths of Near IR and compares this to a calibration model. This produces a real-time measurement of the THC and CBD concentration during extraction. As a bonus, the concentrations of CBN and other minor cannabinoids can be measured at the same time.
Other real-time processes that can be monitored by near-infrared include, extraction of THC and CBD from biomass, decarboxylation of THC and CBD, and conversion of CBD to D8 THC.
Leave a Reply